Abstract
KMT2A, also known as the mixed lineage leukemia (MLL), encodes a lysine-specific histone methyltransferase responsible for chromatin modifications and regulation of gene expression during early development and hemopoiesis through transcriptional activation. Translocations involving KMT2A are among the most common genomic aberrations seen in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (AML), representing a diverse patient population without a robust method for risk stratification. By leveraging RNAseq data and clinical annotation in 220 patients with KMT2A fusions from the TARGET AML 1031 cohort (0-22 years old), we developed DRPPM-PATH-SURVIEOR, a Multiomics Pathway Survival Analysis Explorer, to identify pathways associated with therapeutic resistance and prioritize therapeutic targets in patients at risk for refractory disease.
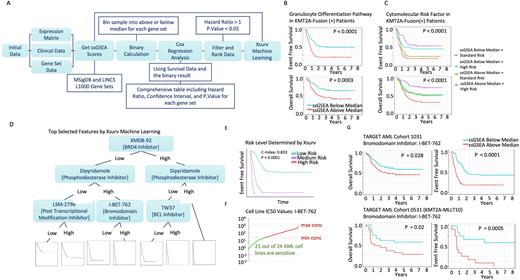
Single sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) was performed on the expression data with the Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB; 32,284 gene sets) and Library of Integrated Network-based Cellular Signatures (LINCS; 31,028 gene sets) L1000 gene sets to derive pathway scores (Figure 1A). Patient samples were categorized based on the derived pathway score into groups of above-median or below-median and then associated with patient survival (OS and EFS) using Cox proportional hazard regression. Significant pathways associated with high risk were selected based on hazard ratio (HR > 1) and P-value (pval < 0.05). From our analysis, increased gene expression in granulocyte differentiation was associated with unfavorable outcomes (Figure 1B). Notably, the granulocyte differentiation pathway score was independent of cytomolecular risk (Figure 1C). Moreover, gene expression associated with increased risk of disease progression in granulocyte differentiation, including TESC, GATA1, HAX1, GATA2, JAGN1, SRP54, and TAL1, were significant in event-free survival, and GATA2, SBTB46, CBFA2T3, JAGN1, and HAX1 were significant in overall survival.
To prioritize a putative therapeutic target that downregulates genes associated with high-risk AML in the KMT2A subgroup, we used, Xsurv, a light gradient boosting machine learning algorithms of XGBoost and LightGBM, to prioritize drug treatment data from the LINC1000 database. The Xsurv model was repeated 100X times with a complexity level of 0.01 to ensure reproducibility - an instance of the selected features is shown in Figure 1D. In general, the risk scores generated by the Xsurv model separated the patient into low-risk (~ 60%), medium-risk (~30%), and high-risk (~10%) patients, with a c-index of 0.8 (p < 0.0001) (Figure 1E). The model identified XMD8-92 and I-BET-762, both Bromodomain inhibitors, as the top feature, appearing in 60 out of the 100 Xsurv runs. Bromodomain proteins BRD3 and BRD4 are components of the super long elongation process (SEC), which plays a role in KMT2A transcription and localization. These results suggest KMT2A-fusions as a potential genetic vulnerability in BRD3/4 targeting. Notably, I-BET-762 was potent in killing KMT2A fusion-positive AML cell lines based on the genomics of drug sensitivity in cancer (GDSC) database (Figure 1F). Furthermore, genes downregulated by the bromodomain inhibitor, I-BET-762, were consistent in predicting the worst prognosis based on OS and EFS in a clinically distinct TARGET AML 0531 cohort (Figure 1G). Taken together, we present an integrative strategy to prioritize pathways for patient risk and identify putative therapeutic targets in high-risk KMT2A fusion-positive AML patients.
Figure 1. A) Schematic workflow of the ssGSEA Pathway Analysis method. B) Event free and overall survival curve with patients classified by a GOBP Granulocyte Differentiation Pathway ssGSEA score based on median cutoff. C) Event Free and overall survival Curve of an interaction model of GOBP Granulocyte Differentiation and the Cytomolecular Risk factor. D) Xsurv survival tree highlighting the top drug hits based on the XGSurv machine learning algorithm. E) Patient risk level determined through the XGSurv model. F) Cell-line sensitivity ranking based on IC50 values of I-BET-762. G) Overall and event free survival curves of KMT2A positive patients in TARGET AAML1031 and AML0531 based on ssGSEA scoring of genes downregulated by the I-BET-762 treatment.
Disclosures
Farrar:Novartis: Other: provision of study materials, medical writing, Research Funding.
OffLabel Disclosure:
XMD8-92 and I-BET-762 were discussed as potential target based on the computational analysis of retrospective data.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal